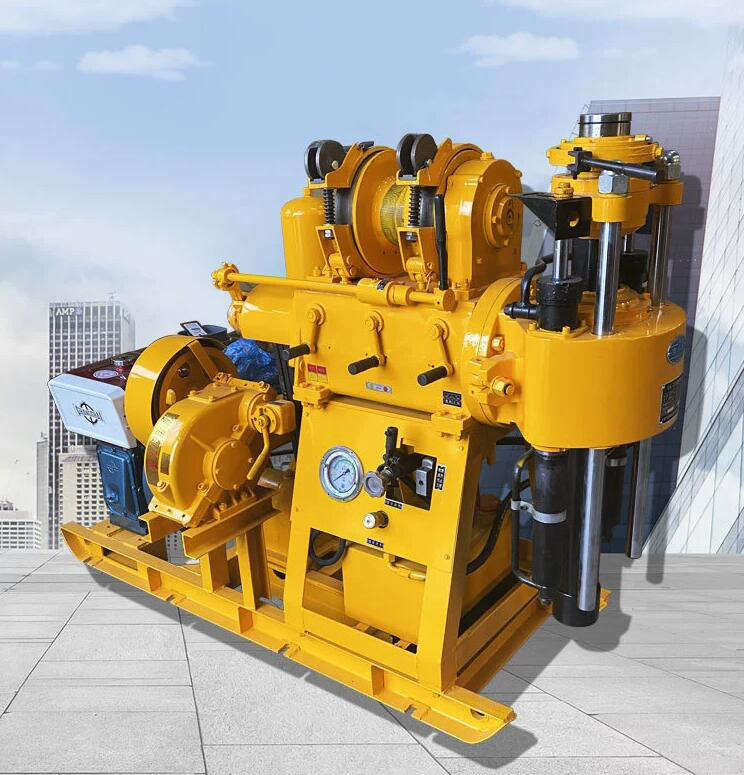
XY-160-C Water well drilling rig high-performance
Top Drive Drilling Rigs: Equipped with a top drive system, these rigs offer more power and efficiency. They can drill deeper and faster compared to table rigs.
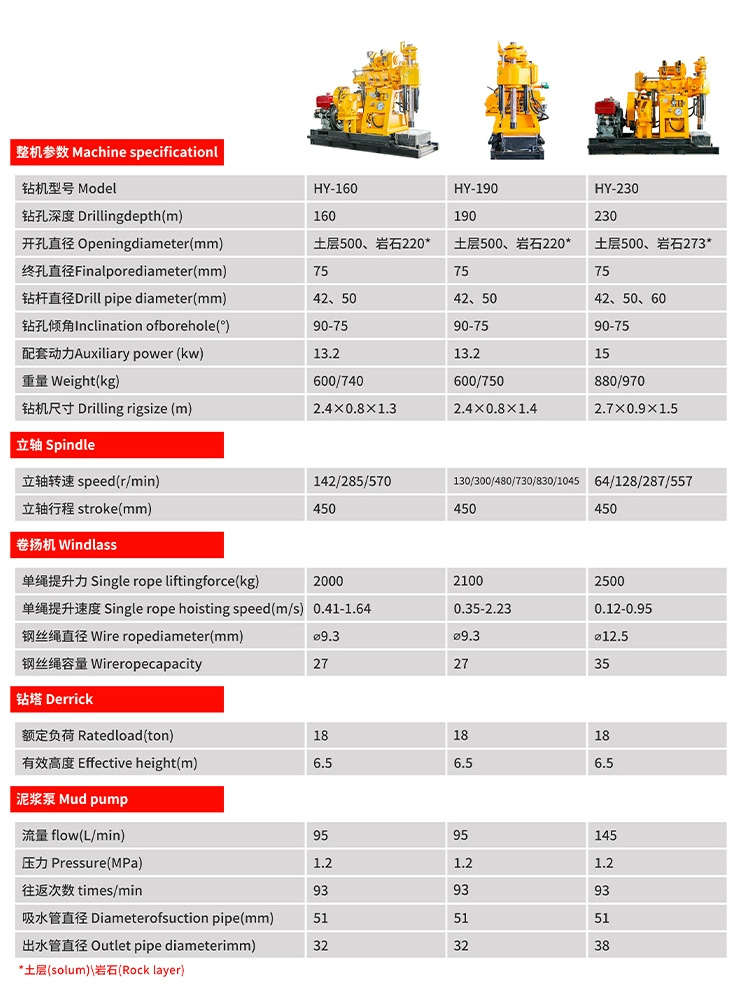
- XY-160-C
- ZHUOXIN
- Water well drilling rig
- shandong.china
- TT, Paypal, Credit card, Western union
- +86-15163766288
- Control System: Modern rigs often include sophisticated control systems for precise drilling operations. The Drilling Operation
Description

Water well drilling rigs are specialized mechanical systems designed for creating holes in the earth's surface to access groundwater. These rigs can be mobile or stationary, and their design varies widely to accommodate different terrains, depths, and drilling methods.

Classification of Drilling Rigs
Table Drilling Rigs: These rigs use a rotary table to turn the drill pipe, allowing the bit to cut through the soil or rock.
Top Drive Drilling Rigs: Equipped with a top drive system, these rigs offer more power and efficiency. They can drill deeper and faster compared to table rigs.

Coiled Tubing Drilling Rigs: Utilizing a continuous loop of tubing, these rigs are efficient for rapid drilling and are often used in re-entry or directional drilling.
Components and Features
Drill Tower or Derrick: A tall structure that supports the drill string and enables efficient drilling operations.
Drill Pipe: A series of tubes that connect the rig surface equipment with the drill bit.
Drill Bit: The component that physically penetrates the ground. There are various types, including diamond bits, carbide bits, and more, chosen based on the geological formation.

Power Source: Rigs are typically powered by diesel engines, but electric and hydraulic options are also common.
Mud Pump: Used to circulate drilling fluid (usually water or mud), which cools the drill bit and brings cuttings to the surface.
Control System: Modern rigs often include sophisticated control systems for precise drilling operations.
The Drilling Operation
Planning and Site Assessment: Before drilling, a thorough assessment of the site and groundwater prospects is essential.

Drilling Operation: The process involves the continuous rotation and pressure application of the drill bit to penetrate the earth.
Removing Cuttings: As the drilling progresses, cuttings are brought up to the surface by the circulating fluid.
Depth and Sample Analysis: Monitoring the depth and collecting soil or rock samples is crucial for understanding the geological profile.
Casing and Completion: After reaching the desired depth, a casing is installed to stabilize the well, followed by wellhead installation.
Geothermal Wells: Drilling for geothermal energy projects.
Hydrogeological Studies: Understanding groundwater flow and composition for environmental and geological studies.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Worker Safety: Implementing rigorous safety standards to prevent accidents and injuries.
Environmental Protection: Ensuring responsible disposal of waste materials and minimizing ecological impact during drilling.

Technological Advancements
Automated drilling systems and advanced monitoring technologies have enhanced the efficiency and safety of water well drilling operations.
Water well drilling rigs play a crucial role in water resource management and development. Their design and functionality are continuously evolving, reflecting advancements in technology and an increasing emphasis on sustainability and environmental protection.
Water well drilling rigs are specialized mechanical systems designed for drilling boreholes into the earth to extract water. These rigs play a crucial role in accessing subterranean water resources, which are vital for residential, agricultural, and commercial uses.
Different Types of Water Well Drilling Rigs
Rotary Drilling Rigs: Utilize a rotary motion to drill, making them effective for deep wells. They are versatile and can work in diverse geological conditions.
Cable Tool Rigs: Employ a pounding action to fracture the earth. Ideal for hard rock formations, they are known for their durability and depth capabilities.

Classification of Drilling Rigs
Table Drilling Rigs: These rigs use a rotary table to turn the drill pipe, allowing the bit to cut through the soil or rock.
Top Drive Drilling Rigs: Equipped with a top drive system, these rigs offer more power and efficiency. They can drill deeper and faster compared to table rigs.

Coiled Tubing Drilling Rigs: Utilizing a continuous loop of tubing, these rigs are efficient for rapid drilling and are often used in re-entry or directional drilling.
Components and Features
Drill Tower or Derrick: A tall structure that supports the drill string and enables efficient drilling operations.
Drill Pipe: A series of tubes that connect the rig surface equipment with the drill bit.
Drill Bit: The component that physically penetrates the ground. There are various types, including diamond bits, carbide bits, and more, chosen based on the geological formation.

Power Source: Rigs are typically powered by diesel engines, but electric and hydraulic options are also common.
Mud Pump: Used to circulate drilling fluid (usually water or mud), which cools the drill bit and brings cuttings to the surface.
Control System: Modern rigs often include sophisticated control systems for precise drilling operations.
The Drilling Operation
Planning and Site Assessment: Before drilling, a thorough assessment of the site and groundwater prospects is essential.

Drilling Operation: The process involves the continuous rotation and pressure application of the drill bit to penetrate the earth.
Removing Cuttings: As the drilling progresses, cuttings are brought up to the surface by the circulating fluid.
Depth and Sample Analysis: Monitoring the depth and collecting soil or rock samples is crucial for understanding the geological profile.
Casing and Completion: After reaching the desired depth, a casing is installed to stabilize the well, followed by wellhead installation.

Geothermal Wells: Drilling for geothermal energy projects.
Hydrogeological Studies: Understanding groundwater flow and composition for environmental and geological studies.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Worker Safety: Implementing rigorous safety standards to prevent accidents and injuries.
Environmental Protection: Ensuring responsible disposal of waste materials and minimizing ecological impact during drilling.

Technological Advancements
Automated drilling systems and advanced monitoring technologies have enhanced the efficiency and safety of water well drilling operations.
Water well drilling rigs play a crucial role in water resource management and development. Their design and functionality are continuously evolving, reflecting advancements in technology and an increasing emphasis on sustainability and environmental protection.
Water well drilling rigs are specialized mechanical systems designed for drilling boreholes into the earth to extract water. These rigs play a crucial role in accessing subterranean water resources, which are vital for residential, agricultural, and commercial uses.
Different Types of Water Well Drilling Rigs
Rotary Drilling Rigs: Utilize a rotary motion to drill, making them effective for deep wells. They are versatile and can work in diverse geological conditions.
Cable Tool Rigs: Employ a pounding action to fracture the earth. Ideal for hard rock formations, they are known for their durability and depth capabilities.
Tags
Get the latest price? We'll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)























